Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
RbNO₃, ⁸⁷Rb (I=3/2) 3QMAS¶
⁸⁷Rb (I=3/2) triple-quantum magic-angle spinning (3Q-MAS) simulation.
The following is an example of the 3QMAS simulation of \(\text{RbNO}_3\), which has three distinct \(^{87}\text{Rb}\) sites. The \(^{87}\text{Rb}\) tensor parameters were obtained from Massiot et al. [1]. In this simulation, a Gaussian broadening is applied to the spectrum as a post-simulation step.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mrsimulator import Simulator, SpinSystem, Site
from mrsimulator.method.lib import ThreeQ_VAS
from mrsimulator import signal_processor as sp
from mrsimulator.spin_system.tensors import SymmetricTensor
from mrsimulator.method import SpectralDimension
Generate the site and spin system objects.
Rb87_1 = Site(
isotope="87Rb",
isotropic_chemical_shift=-27.4, # in ppm
quadrupolar=SymmetricTensor(Cq=1.68e6, eta=0.2), # Cq is in Hz
)
Rb87_2 = Site(
isotope="87Rb",
isotropic_chemical_shift=-28.5, # in ppm
quadrupolar=SymmetricTensor(Cq=1.94e6, eta=1.0), # Cq is in Hz
)
Rb87_3 = Site(
isotope="87Rb",
isotropic_chemical_shift=-31.3, # in ppm
quadrupolar=SymmetricTensor(Cq=1.72e6, eta=0.5), # Cq is in Hz
)
sites = [Rb87_1, Rb87_2, Rb87_3] # all sites
spin_systems = [SpinSystem(sites=[s]) for s in sites]
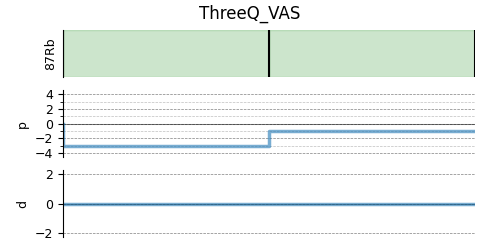
Select a Triple Quantum variable-angle spinning method. You may optionally provide a rotor_angle to the method. The default rotor_angle is the magic-angle.
method = ThreeQ_VAS(
channels=["87Rb"],
magnetic_flux_density=9.4, # in T
spectral_dimensions=[
SpectralDimension(
count=128,
spectral_width=7e3, # in Hz
reference_offset=-7e3, # in Hz
label="Isotropic dimension",
),
SpectralDimension(
count=256,
spectral_width=1e4, # in Hz
reference_offset=-4e3, # in Hz
label="MAS dimension",
),
],
)
# A graphical representation of the method object.
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 2.5))
method.plot()
plt.show()
Create the Simulator object, add the method and spin system objects, and run the simulation.
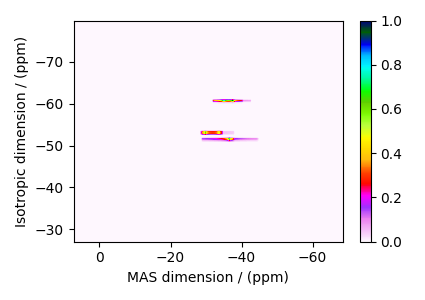
The plot of the simulation.
dataset = sim.methods[0].simulation
plt.figure(figsize=(4.25, 3.0))
ax = plt.subplot(projection="csdm")
cb = ax.imshow(dataset.real / dataset.real.max(), aspect="auto", cmap="gist_ncar_r")
plt.colorbar(cb)
ax.invert_xaxis()
ax.invert_yaxis()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Add post-simulation signal processing.
processor = sp.SignalProcessor(
operations=[
# Gaussian convolution along both dimensions.
sp.IFFT(dim_index=(0, 1)),
sp.apodization.Gaussian(FWHM="0.08 kHz", dim_index=0),
sp.apodization.Gaussian(FWHM="0.22 kHz", dim_index=1),
sp.FFT(dim_index=(0, 1)),
]
)
processed_dataset = processor.apply_operations(dataset=sim.methods[0].simulation)
processed_dataset /= processed_dataset.max()
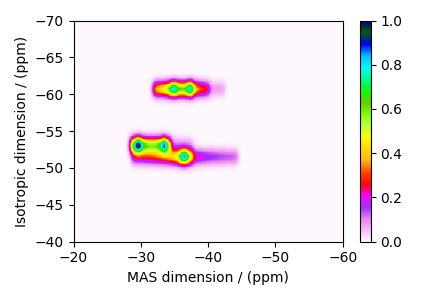
The plot of the simulation after signal processing.
plt.figure(figsize=(4.25, 3.0))
ax = plt.subplot(projection="csdm")
cb = ax.imshow(processed_dataset.real, cmap="gist_ncar_r", aspect="auto")
plt.colorbar(cb)
ax.set_ylim(-40, -70)
ax.set_xlim(-20, -60)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
See also
Simulating site disorder (crystalline) for RbNO3.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.052 seconds)
