Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Rb₂CrO₄, ⁸⁷Rb (I=3/2) SAS¶
⁸⁷Rb (I=3/2) Switched-angle spinning (SAS) simulation.
The following is a Switched-Angle Spinning (SAS) simulation of \(\text{Rb}_2\text{CrO}_4\). While \(\text{Rb}_2\text{CrO}_4\) has two rubidium sites, the site with the smaller quadrupolar interaction was selectively observed and reported by Shore et al. [1]. The following is the simulation based on the published tensor parameters.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mrsimulator import Simulator, SpinSystem, Site
from mrsimulator.method import Method, SpectralDimension, SpectralEvent
from mrsimulator import signal_processor as sp
from mrsimulator.spin_system.tensors import SymmetricTensor
Generate the site and spin system objects.
site = Site(
isotope="87Rb",
isotropic_chemical_shift=-7, # in ppm
shielding_symmetric=SymmetricTensor(zeta=110, eta=0),
quadrupolar=SymmetricTensor(
Cq=3.5e6, # in Hz
eta=0.3,
alpha=0, # in rads
beta=70 * 3.14159 / 180, # in rads
gamma=0, # in rads
),
)
spin_system = SpinSystem(sites=[site])
Use the generic Method class to simulate a 2D SAS spectrum by customizing the method parameters, as shown below.
sas = Method(
channels=["87Rb"],
magnetic_flux_density=4.2, # in T
rotor_frequency=np.inf,
spectral_dimensions=[
SpectralDimension(
count=256,
spectral_width=1.5e4, # in Hz
reference_offset=-5e3, # in Hz
label="70.12 dimension",
events=[
SpectralEvent(
rotor_angle=70.12 * np.pi / 180, # in radians
transition_queries=[{"ch1": {"P": [-1], "D": [0]}}],
)
],
),
SpectralDimension(
count=512,
spectral_width=15e3, # in Hz
reference_offset=-7e3, # in Hz
label="MAS dimension",
events=[
SpectralEvent(
rotor_angle=54.74 * np.pi / 180, # in radians
transition_queries=[{"ch1": {"P": [-1], "D": [0]}}],
)
],
),
],
)
Create the Simulator object, add the method and spin system objects, and run the simulation.
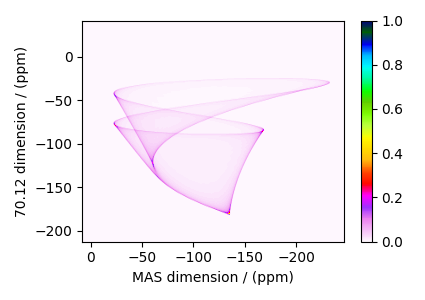
The plot of the simulation.
dataset = sim.methods[0].simulation
plt.figure(figsize=(4.25, 3.0))
ax = plt.subplot(projection="csdm")
cb = ax.imshow(dataset.real / dataset.real.max(), aspect="auto", cmap="gist_ncar_r")
plt.colorbar(cb)
ax.invert_xaxis()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Add post-simulation signal processing.
processor = sp.SignalProcessor(
operations=[
# Gaussian convolution along both dimensions.
sp.IFFT(dim_index=(0, 1)),
sp.apodization.Gaussian(FWHM="0.2 kHz", dim_index=0),
sp.apodization.Gaussian(FWHM="0.2 kHz", dim_index=1),
sp.FFT(dim_index=(0, 1)),
]
)
processed_dataset = processor.apply_operations(dataset=dataset)
processed_dataset /= processed_dataset.max()
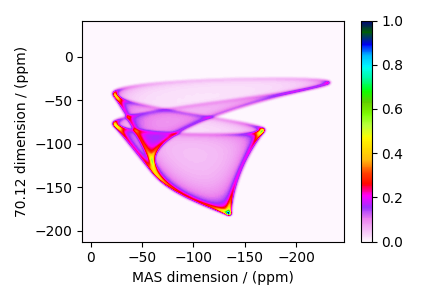
The plot of the simulation after signal processing.
plt.figure(figsize=(4.25, 3.0))
ax = plt.subplot(projection="csdm")
cb = ax.imshow(processed_dataset.real, cmap="gist_ncar_r", aspect="auto")
plt.colorbar(cb)
ax.invert_xaxis()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.913 seconds)
