Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
¹³C 2D MAT NMR of L-Histidine¶
The following is an illustration for fitting 2D MAT/PASS datasets. The example dataset is a \(^{13}\text{C}\) 2D MAT spectrum of L-Histidine from Walder et al. [1]
import numpy as np
import csdmpy as cp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from lmfit import Minimizer
from mrsimulator import Simulator
from mrsimulator.method.lib import SSB2D
from mrsimulator import signal_processor as sp
from mrsimulator.utils import spectral_fitting as sf
from mrsimulator.utils import get_spectral_dimensions
from mrsimulator.utils.collection import single_site_system_generator
Import the dataset¶
host = "https://ssnmr.org/sites/default/files/mrsimulator/"
filename = "1H13C_CPPASS_LHistidine.csdf"
mat_dataset = cp.load(host + filename)
# For the spectral fitting, we only focus on the real part of the complex dataset.
mat_dataset = mat_dataset.real
# Convert the coordinates along each dimension from Hz to ppm.
_ = [item.to("ppm", "nmr_frequency_ratio") for item in mat_dataset.dimensions]
When using the SSB2D method, ensure the horizontal dimension of the dataset is the isotropic dimension. Here, we apply an appropriate transpose operation to the dataset.
mat_dataset = mat_dataset.T # transpose
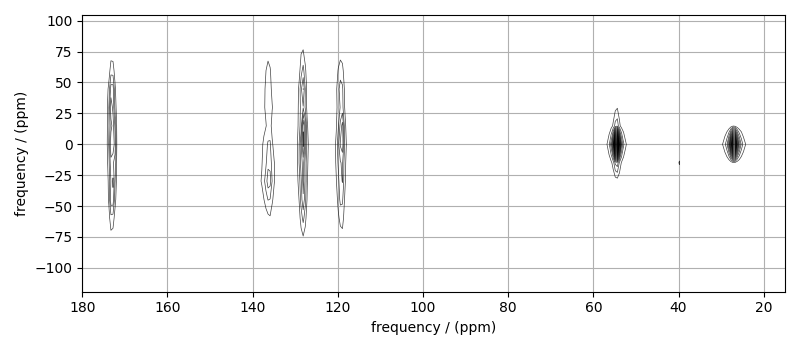
# plot of the dataset.
max_amp = mat_dataset.max()
levels = (np.arange(24) + 1) * max_amp / 25 # contours are drawn at these levels.
options = dict(levels=levels, alpha=0.75, linewidths=0.5) # plot options
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 3.5))
ax = plt.subplot(projection="csdm")
ax.contour(mat_dataset, colors="k", **options)
ax.set_xlim(180, 15)
plt.grid()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Estimate noise statistics from the dataset
coords = mat_dataset.dimensions[0].coordinates
# noise_region = np.where(np.logical_and(coords > 65e-6, coords < 110e-6))
noise_region = np.where(np.logical_and(coords < 110e-6, coords > 65e-6))
noise_data = mat_dataset[noise_region]
plt.figure(figsize=(3.75, 2.5))
ax = plt.subplot(projection="csdm")
ax.imshow(noise_data, aspect="auto", interpolation="none")
plt.title("Noise section")
plt.axis("off")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
noise_mean, sigma = noise_data.mean(), noise_data.std()
noise_mean, sigma
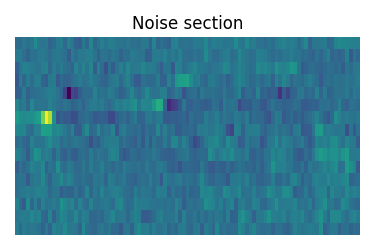
(<Quantity -0.00846708>, <Quantity 0.5979741>)
Create a fitting model¶
Guess model
Create a guess list of spin systems.
shifts = [120, 128, 135, 175, 55, 25] # in ppm
zeta = [-70, -65, -60, -60, -10, -10] # in ppm
eta = [0.8, 0.4, 0.9, 0.3, 0.05, 0.05]
spin_systems = single_site_system_generator(
isotope="13C",
isotropic_chemical_shift=shifts,
shielding_symmetric={"zeta": zeta, "eta": eta},
abundance=100 / 6,
)
Method
Create the SSB2D method.
# Get the spectral dimension parameters from the experiment.
spectral_dims = get_spectral_dimensions(mat_dataset)
PASS = SSB2D(
channels=["13C"],
magnetic_flux_density=9.395, # in T
rotor_frequency=1500, # in Hz
spectral_dimensions=spectral_dims,
experiment=mat_dataset, # add the measurement to the method.
)
Guess Spectrum
# Simulation
# ----------
sim = Simulator(spin_systems=spin_systems, methods=[PASS])
sim.run()
# Post Simulation Processing
# --------------------------
processor = sp.SignalProcessor(
operations=[
# Lorentzian convolution along the isotropic dimensions.
sp.FFT(dim_index=0),
sp.apodization.Exponential(FWHM="50 Hz"),
sp.IFFT(dim_index=0),
sp.Scale(factor=2122600),
]
)
processed_dataset = processor.apply_operations(dataset=sim.methods[0].simulation).real
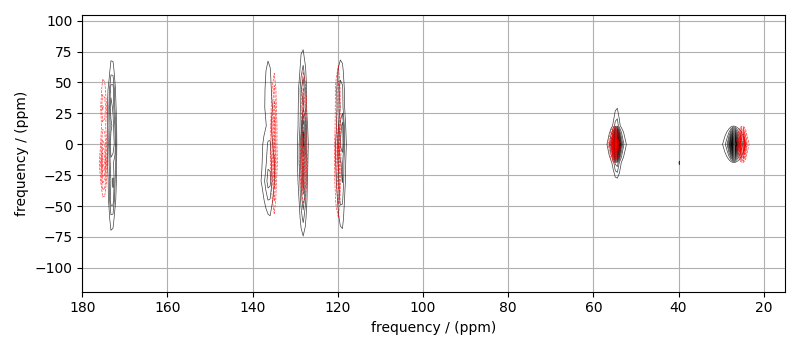
# Plot of the guess Spectrum
# --------------------------
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 3.5))
ax = plt.subplot(projection="csdm")
ax.contour(mat_dataset, colors="k", **options)
ax.contour(processed_dataset, colors="r", linestyles="--", **options)
ax.set_xlim(180, 15)
plt.grid()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Least-squares minimization with LMFIT¶
Use the make_LMFIT_params() for a quick
setup of the fitting parameters.
params = sf.make_LMFIT_params(sim, processor)
print(params.pretty_print(columns=["value", "min", "max", "vary", "expr"]))
Name Value Min Max Vary Expr
SP_0_operation_1_Exponential_FWHM 50 -inf inf True None
SP_0_operation_3_Scale_factor 2.123e+06 -inf inf True None
sys_0_abundance 16.67 0 100 True None
sys_0_site_0_isotropic_chemical_shift 120 -inf inf True None
sys_0_site_0_shielding_symmetric_eta 0.8 0 1 True None
sys_0_site_0_shielding_symmetric_zeta -70 -inf inf True None
sys_1_abundance 16.67 0 100 True None
sys_1_site_0_isotropic_chemical_shift 128 -inf inf True None
sys_1_site_0_shielding_symmetric_eta 0.4 0 1 True None
sys_1_site_0_shielding_symmetric_zeta -65 -inf inf True None
sys_2_abundance 16.67 0 100 True None
sys_2_site_0_isotropic_chemical_shift 135 -inf inf True None
sys_2_site_0_shielding_symmetric_eta 0.9 0 1 True None
sys_2_site_0_shielding_symmetric_zeta -60 -inf inf True None
sys_3_abundance 16.67 0 100 True None
sys_3_site_0_isotropic_chemical_shift 175 -inf inf True None
sys_3_site_0_shielding_symmetric_eta 0.3 0 1 True None
sys_3_site_0_shielding_symmetric_zeta -60 -inf inf True None
sys_4_abundance 16.67 0 100 True None
sys_4_site_0_isotropic_chemical_shift 55 -inf inf True None
sys_4_site_0_shielding_symmetric_eta 0.05 0 1 True None
sys_4_site_0_shielding_symmetric_zeta -10 -inf inf True None
sys_5_abundance 16.67 0 100 False 100-sys_0_abundance-sys_1_abundance-sys_2_abundance-sys_3_abundance-sys_4_abundance
sys_5_site_0_isotropic_chemical_shift 25 -inf inf True None
sys_5_site_0_shielding_symmetric_eta 0.05 0 1 True None
sys_5_site_0_shielding_symmetric_zeta -10 -inf inf True None
None
Solve the minimizer using LMFIT
opt = sim.optimize() # Pre-compute transition pathways
minner = Minimizer(
sf.LMFIT_min_function,
params,
fcn_args=(sim, processor, sigma),
fcn_kws={"opt": opt},
)
result = minner.minimize()
result
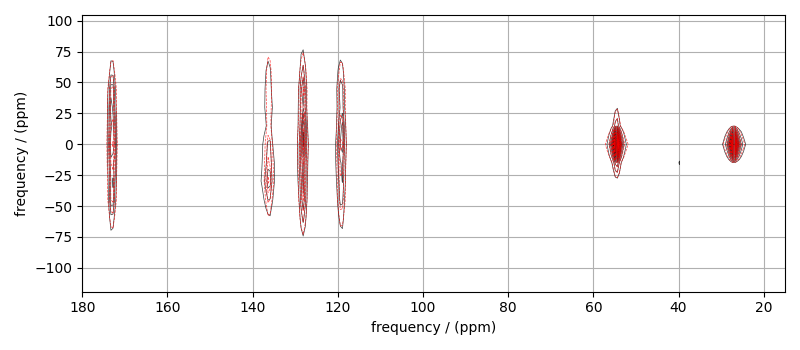
The best fit solution¶
best_fit = sf.bestfit(sim, processor)[0].real
# Plot of the best fit solution
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 3.5))
ax = plt.subplot(projection="csdm")
ax.contour(mat_dataset, colors="k", **options)
ax.contour(best_fit, colors="r", linestyles="--", **options)
ax.set_xlim(180, 15)
plt.grid()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 25.399 seconds)
